Robots#
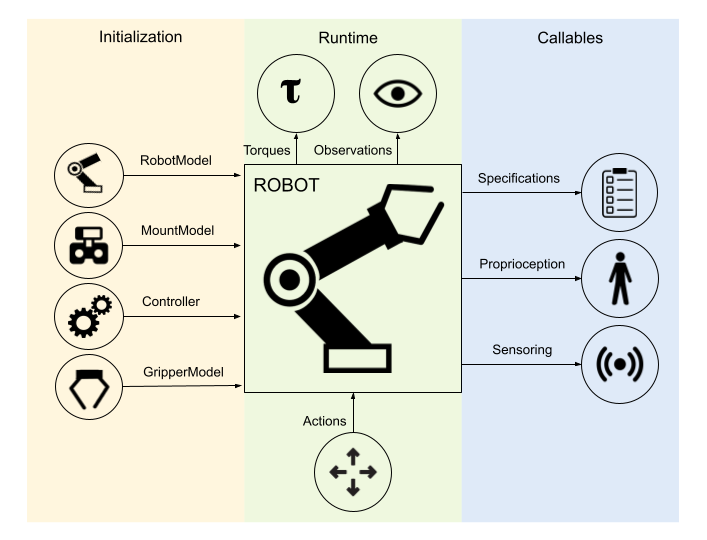
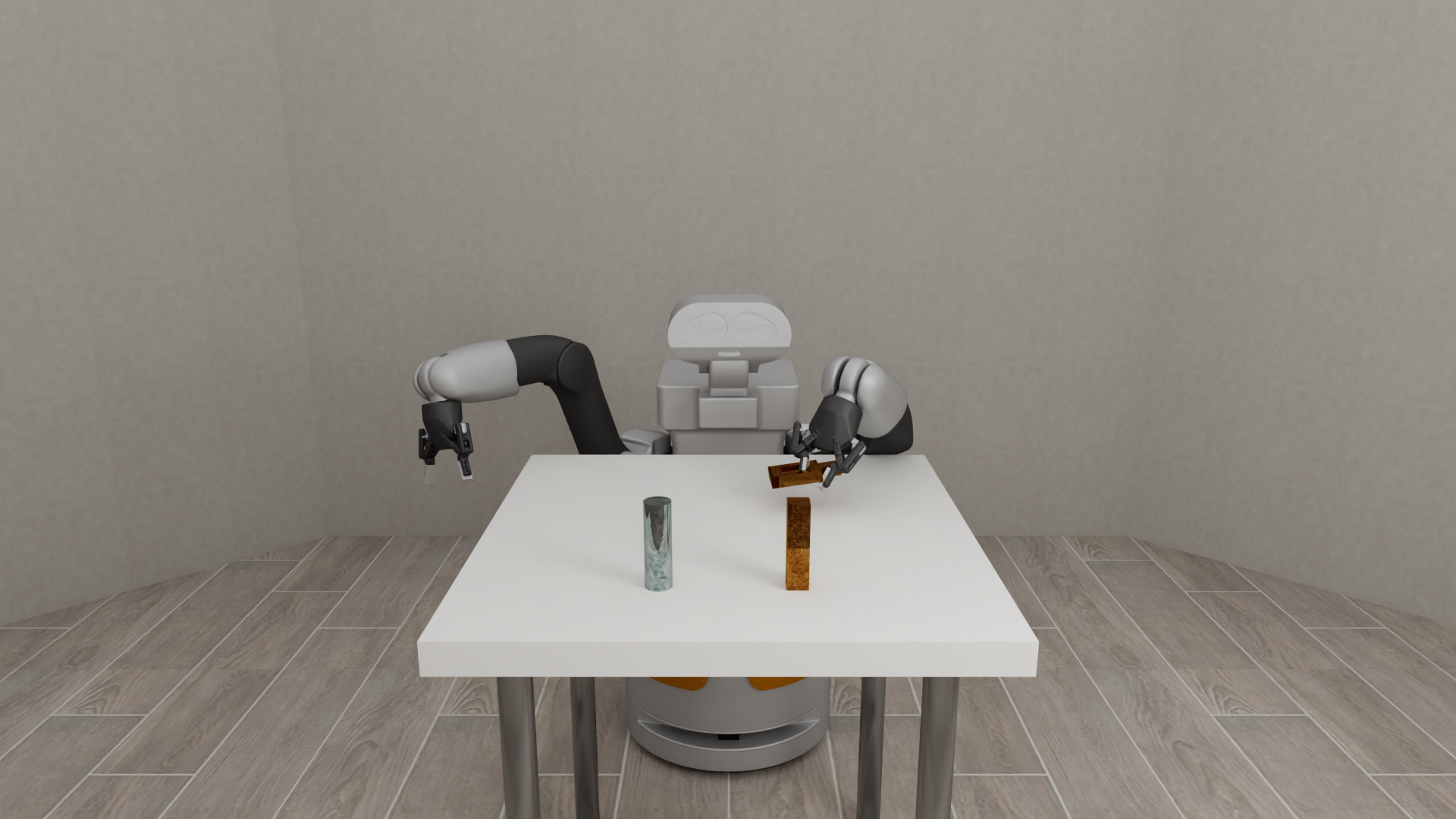
Robots are a key component in robosuite, and serve as the embodiment of a given agent as well as the central interaction point within an environment and key interface to MuJoCo for the robot-related state and control. robosuite captures this level of abstraction with the Robot-based classes, with support for both single-armed and bimanual variations, as well as robots with mobile manipulation capabilities, including both legged and wheeled variants. In turn, the Robot class is centrally defined by a RobotModel, RobotBaseModel, GripperModel, and Controller(s). Subclasses of the RobotModel class may also include additional models as well; for example, the ManipulatorModel class also includes GripperModel(s) (with no gripper being represented by a dummy class).
The high-level features of robosuite’s robots are described as follows:
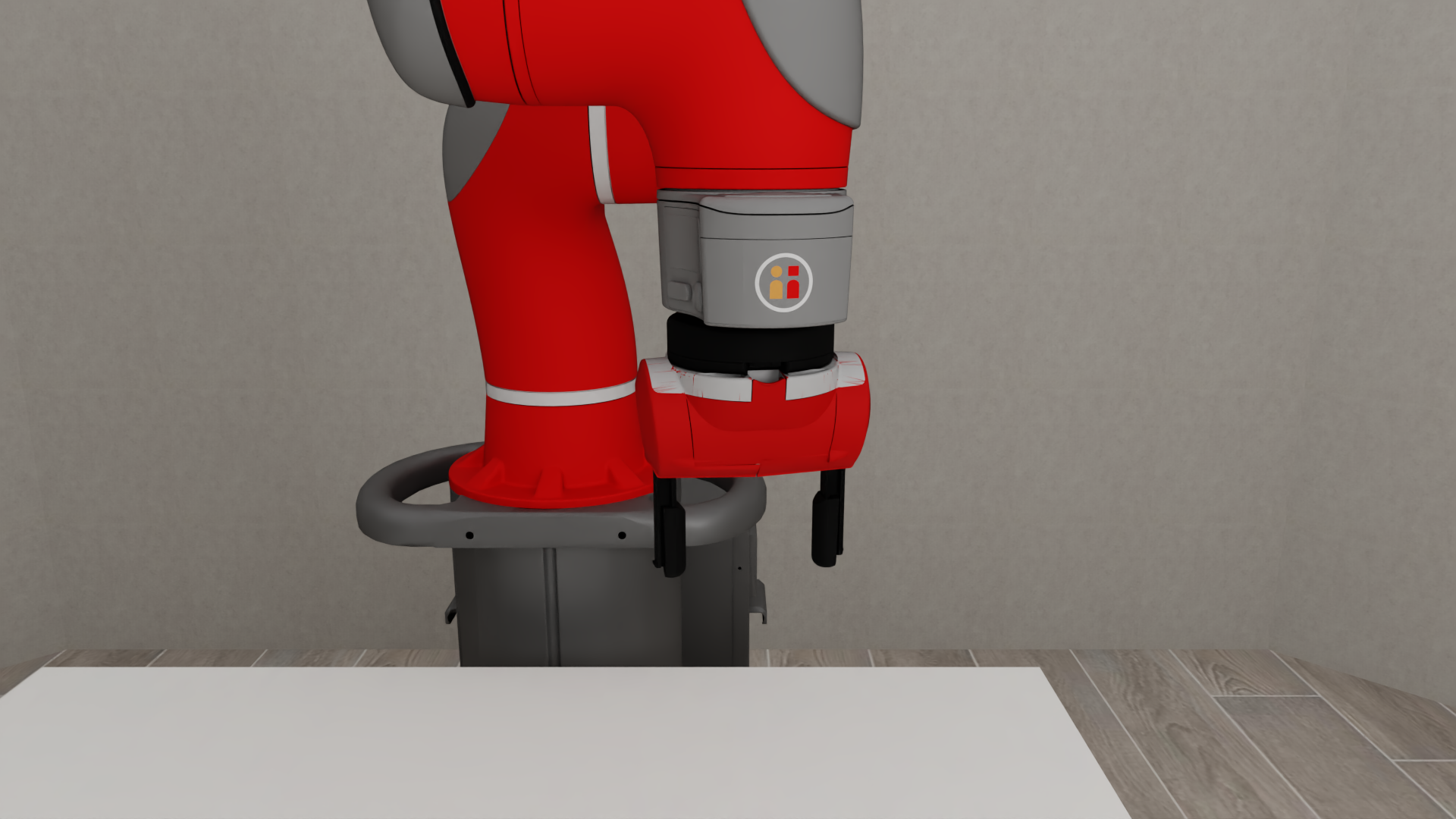
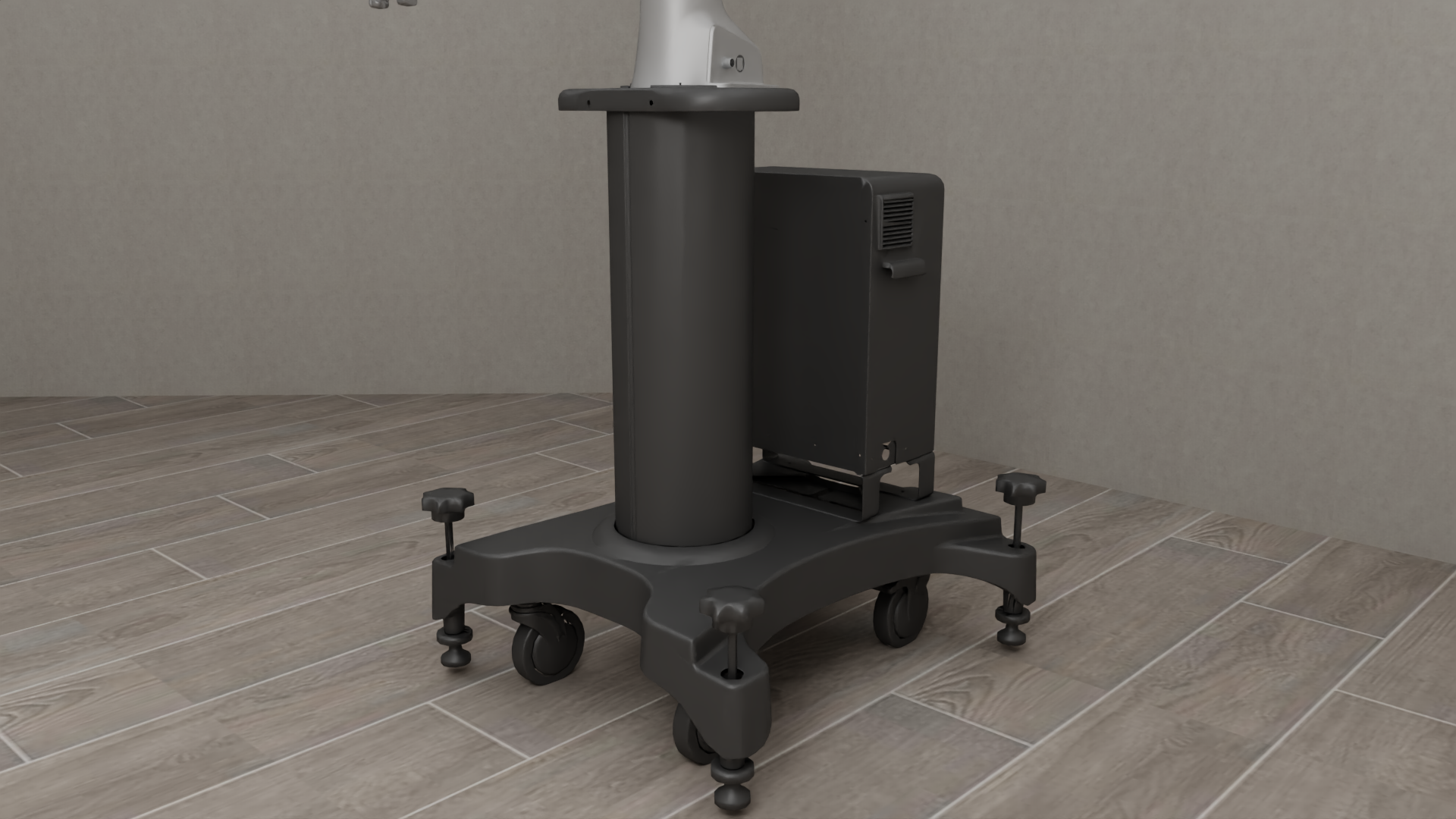
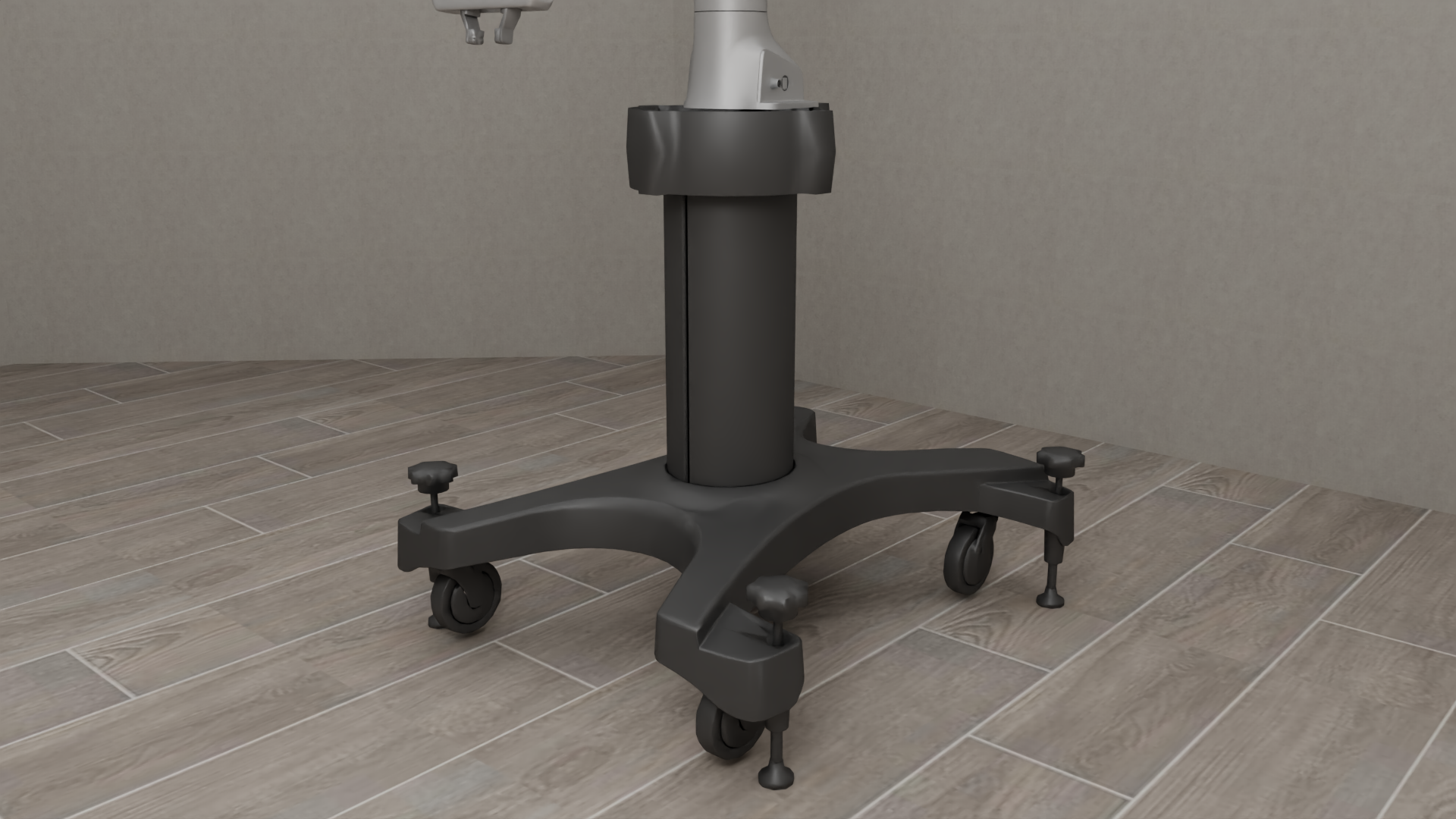
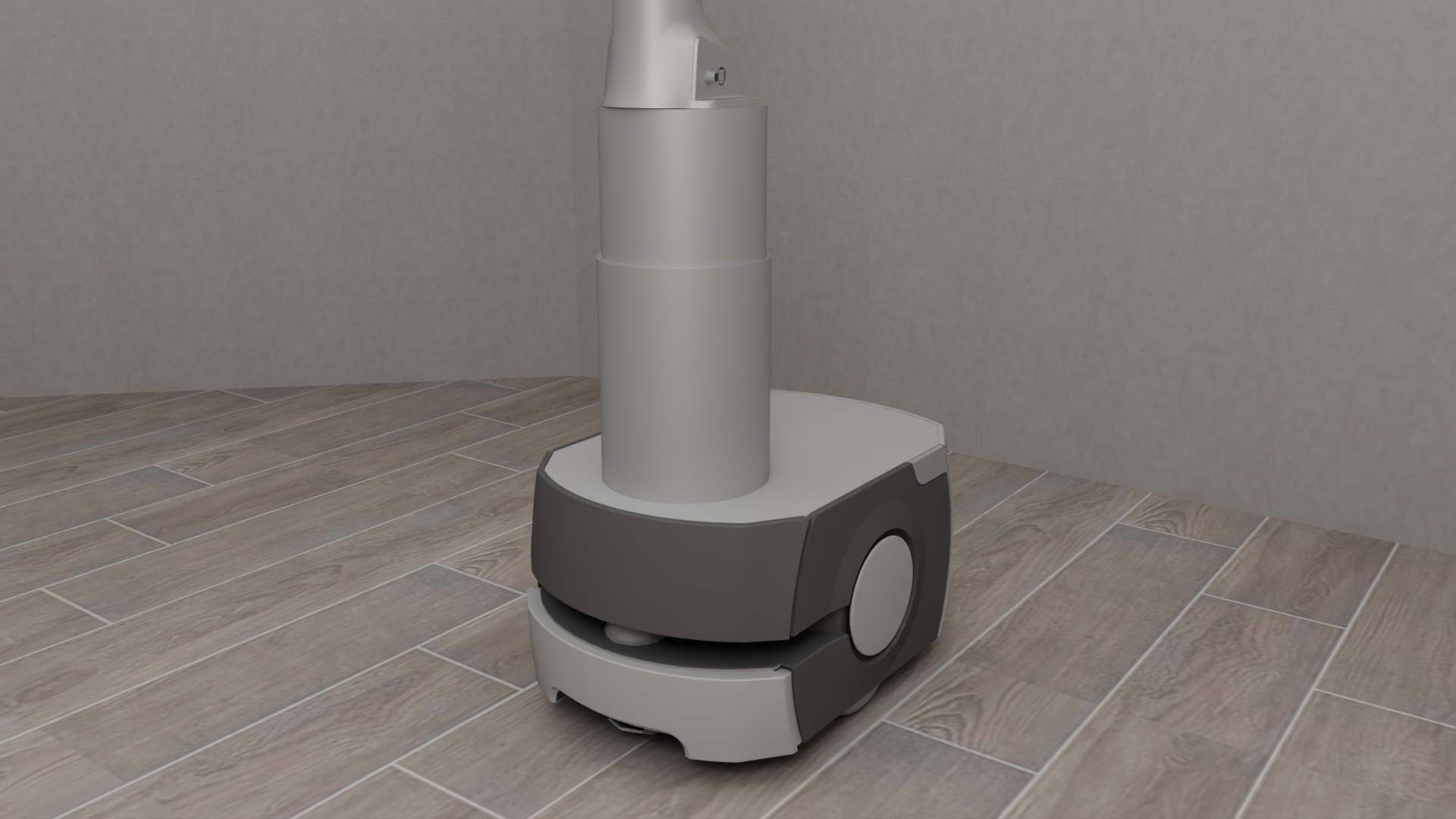
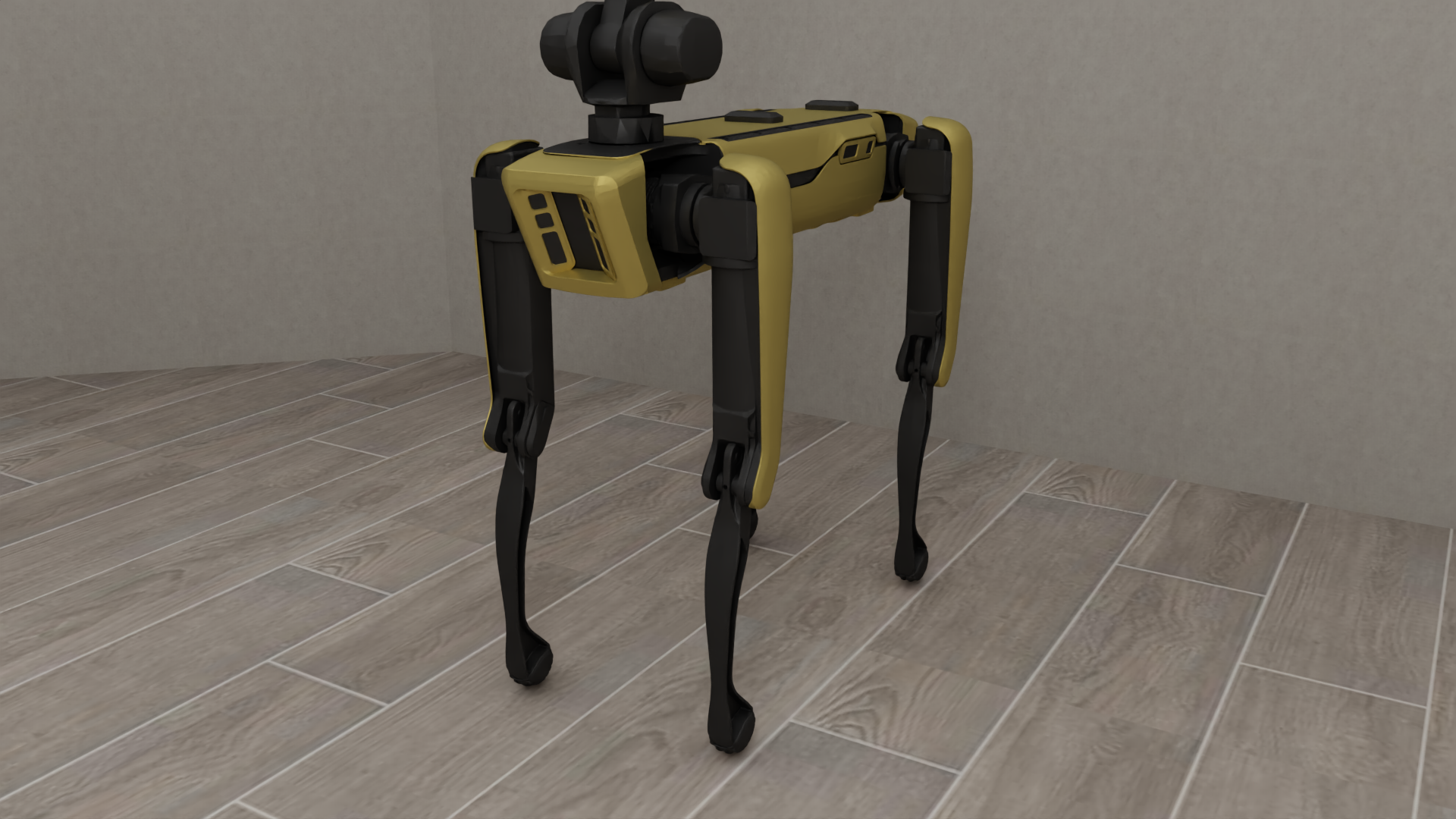
Diverse and Realistic Models: robosuite provides models for 10 commercially-available robots (including the humanoid GR1 Robot), 9 grippers (including the inspire dexterous hand model), 4 bases (including the Omron wheeled mobile base), and 6 body-part controllers, with model properties either taken directly from official product documentation or raw spec sheets. An additional 8 robots, 8 grippers, and 3 bases can be installed separately from the robosuite-models repository.
Modularized Support: Robots are designed to be plug-n-play – any combinations of robots, models, and controllers can be used, assuming the given environment is intended for the desired robot configuration. Because each robot is assigned a unique ID number, multiple instances of identical robots can be instantiated within the simulation without error.
Self-Enclosed Abstraction: For a given task and environment, any information relevant to the specific robot instance can be found within the properties and methods within that instance. This means that each robot is responsible for directly setting its initial state within the simulation at the start of each episode, and also directly controls the robot in simulation via torques outputted by its controller’s transformed actions.
Usage#
Below, we discuss the usage and functionality of the robots over the course of its program lifetime.
Initialization#
During environment creation (suite.make(...)), individual robots are both instantiated and initialized. The desired RobotModel, RobotBaseModel, and Controller(s) (where multiple and/or additional models may be specified, e.g. for manipulator bimanual robots) are loaded into each robot, with the models being passed into the environment to compose the final MuJoCo simulation object. Each robot is then set to its initial state.
Runtime#
During a given simulation episode (each env.step(...) call), the environment will receive a set of actions and distribute them accordingly to each robot, according to their respective action spaces. Each robot then converts these actions into low-level torques via their respective controllers, and directly executes these torques in the simulation. At the conclusion of the environment step, each robot will pass its set of robot-specific observations to the environment, which will then concatenate and append additional task-level observations before passing them as output from the env.step(...) call.
Callables#
At any given time, each robot has a set of properties whose real-time values can be accessed at any time. These include specifications for a given robot, such as its DoF, action dimension, and torque limits, as well as proprioceptive values, such as its joint positions and velocities. Additionally, if the robot is enabled with any sensors, those readings can also be polled as well. A full list of robot properties can be found in the Robots API section.
Models#
robosuite is designed to be generalizable to multiple robotic domains. The current release focuses on manipulator robots. For adding new robots, we provide a rudimentary guide on how to import raw Robot and Gripper models (based on a URDF source file) into robosuite.
Manipulators#
Grippers#
Bases#
Create Your Own Robot#
As of v1.5, users can create composite robots to match their specification. Specificially, arms, grippers, and bases can be swapped to create new robots configurations. We also provide several other robot models in an external repo. For more information, please refer to here.